SCIENTIFIC INTEREST
** יעדמ
ןיינע יאשונ

|
םירחא רוע-יצווקו יתליאה ןפיטק
לש תויסולכואה תייגולויבו הלידגה
תויביטימירפ תונוכת םיארמ םה
דחמ .םנימב םידחוימ םייח-ילעב םה םי-ידופיק
םידייוצמ םה ךדיאמ .תיזכרמ םיבצע
תכרעמ וא םייניע , שאר רדעה,לגועמ ףוג -
-"םימ-ילגר" -הליעי
העונת תכרעמ ,(וטסירא סנפ)תללכושמ הסיעל תכרעמב
,תומאות ריג תוחול יושע ,ירטמיס
םדליש ;םתוצקב הדמצה רותפכש םירירוניצ
ןגלוק יביסב 'תורופת'ה ,ןפקיהב
תולדג ןמזב ובו ןמזה לכ תופסונ תושדחש
.םתוצקב הדח תבצש -םיתבצוק -םינטקו
,םידחו םילודג םיצוקב םיניוזמ םה .םישימג
ןימ-תת ולש ,תינייקוא הצופת לעב
םייסרא םיתבצוק לעב םי-דופיק אוה ןפיטקה
.םינוש םימצעב ומצע תוסכל גהונה
יתליא
םיאנתב ותלידגו וייח חרוא תא
,םינש המכ ךשמב הז ידוחי ןימ-תת יתרקח
.םייחה יאנתב יולת לכה ,תחא הנשמ
תוחפ םיתיעלו יתנש-בר אוה םיתיעל .םינוש
|
|

|
Growth and Population
biology of the short-spined sea-urchin Tripneustes gratilla elatensis
Sea-urchins (classis Echinoida)
are a unique kind of invertebrate animals. In one aspect, they show primitive
traits -- circular shape, lack of head, eyes and central nervous center.
On the other hand, they are equipped with very complex chewing apparatus
("Aristotle's lantern"), very efficient locomotory system, hydraulic
tube-feet -- tubular pipes emerging from small hole -- called ambulacra
- with vaccum attachment discs at their end; Their skeleton is a symmetrical
structure made of close-fitting calcareous plates - which grow in a definte
pattern, constantly adding more and more plates - held together by flexible
collagenous fibers. They are armed with thick spines, and smaller spines
ending with sharp and sometimes poisnous pincers (called pedicellaria)
Tripneustes gratilla
is a common indo-pacific regular echinoid of the sea-urchin family
Toxopneustidae - bearing toxic pedicellaria. It covers itself with
debris from bits of coral to sand grains. Spines are short and harmless
so the tube feet are easily observable. Pedicellaria are trigeminous globiferous.
Average size in the Red Sea is about 70 mm, reaching 130 mm. I have described
a new subspecies -- T. g. elatensis
-- endemic to the Red Sea (ref. 5, below)
I have studied this sub-species
for several years, and found that growth rates depend on available resources
- at optimum condition T. g. elatensis obtains a maximal size of
60 mm in 150 days, while under limiting condition - low nutrition and presence
of predators - they remain stunted for elongated periods. In has been shown
that in shores exposed to winter storms they breed in their first year,
before being washed-out by the waves, while in an adjacent, more protected
shore, they adopt a multi-annual life pattern (ref. 12, 16 below).
|
|
םיה-ידופק דלש לש יטמואנפה
יפואה
תינוציח הפילקכ יושע אוה :דחאכ
תוילוח-ילעבו תוילוח-ירסח ןיב םיידוחי םה םי-ידופיק ידלש
םיימינפ םיינכמ תוחוכמ עפשומ
דלשה הנבמ יכ עצוה .ימינפ לזונב םייורש םיימינפה םהירבאשכ
תוינכמה תונוכתהו םימה-ילגר ירירש
,םיינוציחו -דלשל יעמה תא םירשוקה םיילאירטנזמ םיטוח
רתוי תויהל םיטונ קזח ינכמ ץחלל
םינותנה םי-ידופיק .דלשה תוחול תא םיחאמה ןגלוקה יביס לש
.הלאכ םיצחל אלל הביבסב םייחה
הלא רשאמ םיחטושמ
לש העפשהה תא חיכוהל ןויסנבו
,יתליא ןפיטקב ריגה תעקשהו הלידגה יבצקב דקמתה ירקחמ
דלשה תוחול לש הכימתה רדעהב םג
יכ יתאצמ .םיה-דופיק לש תיפוסה הרוצה לע םיינכמ םיצחל
.ריגה תעקשהל ינגרוא סקירטמ הווהמה
,הכרה תפטעמל תודוה ,ותרוצ תא דלשה רמוש
,תוכומס תויחול ןיבש םירפתב םיאורש
"ןובסה תועוב" םגד אוה תיטמואינפה הזיתופהל החכוה
ואיבה תופסונ תויודעו הז .תינגרואה
תפטעמה לש הלידגל תינשמ איה ריגה תעקשה יכ דיעמה
.םי-ידופיק לש הזנגופרומהו הלידגל
"ינכמ-ויב לדומ" עיצהל יתוא
|
|

|
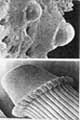
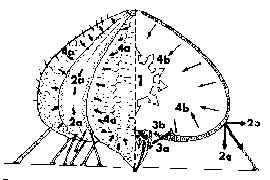
Pneumatic nature of the echinoid skeletons
Sea-urchin skeletons (tests) are
unique among vertebrates and invertebrates alike: They are formed as an
outer shell, containing inner fluid. It has been suggested that the test
is affected by mechanical forces, exerted by inner -- thethering mesenterial
threads -- and outer -- tubefeet muscles and the mechanical properties
of the collagen fibers that connect the test plates. Under low mechanical
activity the test tends to be globular, while under strong adherence the
test is flat.
 A chemically decalcified dead sea-urchin
retains its shape, proving that the overall shape of the sea-urchin is
supported by the pneumatic properties of the soft tissue.
A chemically decalcified dead sea-urchin
retains its shape, proving that the overall shape of the sea-urchin is
supported by the pneumatic properties of the soft tissue.
A special emphasis in my studies were observations and
experiments dealing with the skeleton growth and calcification of the test,
trying to demonstrate the influence of mechanical pressure and forces applied
by the contractile and -- tissues on the final shape. I showed that even
without the support of the hard plates, the sea urchin form retains it
typical shape, due to the soft tissue envelope, which acts as a matrix
to the calcium carbonate plates. An evidence to the pneumatic hypothesis
is the "soap-bubble" curvature pattern of the plates' edge, indicating
that inner pressure and outer surface tension of the plates' envelope are
primary to the calcification process. This and other evidence urged me
to propose a "bio- mechanical" model for the growth and morphogenesis
of sea urchins (ref. 10). The model was tested experimentally by various
scientists.
|
|
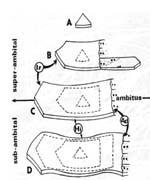  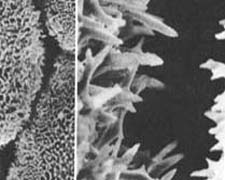
Left: the reversal curvature pattern of echinoid skeletal
plates, showing in the plate edge and earlier growth-lines. Right: a gap
between two neighboring plates in a living test, induces rapid growth of
needle-like 'trabeculae', proving that available space enhances rapid growth.
Middle: graphic presentation of the "mechanical model".
|
|
 Two types of deformed T. gratilla under
pollution
Two types of deformed T. gratilla under
pollution
|
םוהיז יאנתב יתליאה ןפיטקה
ידלשב םיתווע |
|

|
Deformities of sea-urchin under pollution
conditions.
Mass-deformities (up to 70% urchins were affected)
of two types were shown in Tripneustes gratilla under pollution
conditions, in the Gulf of Eilat. The apparent cause seems to be chemicals
aiming to prevent calcium carbonate clogging of pipe systems in a local
power-plant (ref. 2) or hotel laundry (6). The deformities are believed
to result from less calcification and softening of the mechanical tissues
- inter-plate collagen fibers, inner muscles etc. These observations seem
to support the proposed model.
|
|
|
תופדצו תונוזלח - תוימי
תוכיכר לש היגולויבה |
|

|
The biology of marine mollusca
The Gulf of Eilat (Aqaba) has a typical Indo-Pacific
fauna, with large amount of endemism. Pollution in the northern part of
the Gulf limits the number of living species. I have followed the Gulf
mollusc fauna for over thirty years, and published semi-popular reports
and lists. Lately I created a website, as data base of the mollusca of the Gulf of Aqaba (Eilat Gulf):
Gulf of Aqaba Mollusca dbase
|
|

|
םינימ ןווגמ לע םוהיז תעפשה
םיסלכאמה םירוציה תרבח לש םינימה
ןווגמ תא - ינש ראות תארקל רקחמב - יתרקח
האצותכ ,ןווגמה דאמ דרוי םוהיז
יאנתב יכ יתאצמ .תליא ץרפמב םיתמ םיגומלא
.םייוצר-תוחפ ,םירחא םינימ לש
תוטלתשהו םידחא םירוצי לש התומתמ
|
|

|
The effect of pollution on the species diversity
I studied the species diversity of invertebrate
community on dead stony corals, aiming to demonstrate the influence of
pollution on the community (ref. 11).
|
|
עבט יאשונב הארוהו הכרדה
תליא רוזיאב עבטה תנגהל הרבחב
חקפו ךירדמכ תובר םינש יתתרש
םירמאמ בר רפסמ יתבתכ .הדשב הכרדהו
םייכונח םיאשונב יתיחמתהו
:םשב םידליל רופיס רואל יתאצוה
םג הנורחאל .תירבעב - הלא םיאשונב
וילא
שולג .טנרטניאה תשרב "תרוחש לחנב רואזוניד"
|
|
Guiding and teaching nature
I have served many years as warden and guide in
the Nature Conservation organization, the Society for the Protection of
Nature, I dedicated much effort to the develope a didactic approach to
field teaching and study. I wrote many articles -- in Hebrew -- on this
topic.
|
|
SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS
1979-1995
- Ben-Eliahu, N. & J. Dafni
(1979) A new reef building serpulid genus and species from Elat and the
Red Sea, with notes on other gregarious tube worms from Israeli waters.Isr.
J. Zool. 28:199-208.
- Dafni, J.(1980) Abnormal growth patterns in the
sea urchin Tripneustes cf. gratilla (L.) under pollution
(Echinodermata: Echinoidea). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 47:259-279.
- Dafni, J. (1982) Skeletal deformations in the
sea urchin Tripneustes gratilla (L.) under pollution conditions
in the Gulf of Eilat, Red Sea. in: Echinoderms - Proceeding of the
Fourth International Conference,Tampa Bay, September 1981 (Ed. J.M. Lawrence),
A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam. pp. 69.
- Dafni, J.& J. Erez (1982) Differential growth
in Tripneustes gratilla (Echinoidea). in: Echinoderms: Proceeding
of the Fourth Intenational Conference, Tampa Bay, September 1981(Ed.
J.M. Lawrence), A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam. pp . 71-75.
- Dafni, J. (1983a) A new sub-species of Tripneustes
gratilla (L.) from the northern Red Sea (Echinodermata: Echinoidea:
Toxopneustidae). Isr. J. Zool., 32:1-12.
- Dafni, J.(1983b) Aboral depressions in the tests
of the sea urchin Tripneustes cf. gratilla (L.) in the Gulf
of Eilat, Red Sea. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 67:1-15.
- Dafni, J.& A. Diamant (1984) School-oriented
mimicry, a new type of mimicry in fishes. Mar.Ecol. Prog. Ser.,
20:45-50.
- Dafni, J. (1985) Effect of mechanical stress
on the calcification pattern in regular echinoids. in: Echinodermata
- Proceeding of the Fifth International Echinoderm Conference, Galway,
September 1984 (Eds. B.E. Keegan and B.D.S. O'Connor), A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam.
pp. 233-236.
- Dafni, J. (1986a) A biomechanical model for the
morphogenesis of echinoid tests. Paleobiology, 12:143-160.
- Dafni, J. (1986b) Echinoid Skeletons as Pneu
Structures. Konzepte SFB 230, Universitat Tubingen und Stuttgart.
Stuttgart, 13:9-96.
- Dafni, J.& L. Fishelson (1986) Effect of
pollution on the community structure of animals associated with dead corals
in Eilat (Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea). In: Environmental Quality and Ecosystem
Stability, Proc. Third Intern. Conf. of the Israeli Ecological Society,
(Ed. Z. Dubinsky & Y. Steinberger). Bar Ilan University Press, Ramat
Gan, Israel. Vol III/B; pp. 849-858.
- Dafni, J.& R. Tobol. (1986/87) Population
structure patterns of a common Red Sea echinoid (Tripneustes gratilla
elatensis)/Isr. J. Zool., 34:191-204.
- Dafni, J.& J. Erez (1987a) Skeletal calcification
patterns in the sea urchin Tripneustes gratilla elatensis: I. Basic
patterns. Mar. Biol. 95:275-287.
- Dafni, J.& J. Erez (1987b) Skeletal calcification
patterns in the sea urchin Tripneustes gratilla elatensis: II. Effect
of various treatments. Mar. Biol. 95:289-297.
- Dafni, J. (1988) A biomechanical approach to
the ontogeny and phylogeny of echinoids. in: C.R.C. Paul & A.B. Smith
(Eds.)Echinoderm Phylogeny and Evolutionary Biology. Oxford University
Press, Oxford. pp. 175-188.
- Dafni, J. (1992) Growth rate of the sea urchin
Tripneustes gratilla elatensis. Isr. J. Zool., 38:25-33.
- Dafni, J. (1995) The need for Damaged Reef Reclamation
and Restoration. In: Proc. International Conference: The Ecosystem of
the Gulf of Aqaba in Relation to the enhanced Economical Development and
the Peace Process II - Eilat, Jan 30th - Feb 2nd, 1995, 84-86
|
. |
"Routes and Trails
in the Eilat Region"
Gefen Publications, Jerusalem
(1995).
A guide book -- in English --
describing 30 foot and car trails in the mountains of Eilat Region:
|
 |
"Gulf of Eilat, from the
Red Sea to the red line..."
A comprehensive account of the
natural and human history of the Gulf of Eilat (Gulf of Aqaba), with reference
to its endangered future.
Tcherikover Publ. House.,Tel-Aviv
In Hebrew: "...ופוס
דעו ףוס-םימ ,תליא ץרפמ"
|
|
|
|





