Scientific
interests

|
Pneumatic nature
of the echinoid skeletons
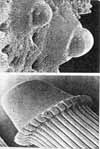
Sea-urchin
skeletons (tests) are unique among vertebrates and invertebrates alike:
They are formed as an outer shell, containing inner fluid. It has been
suggested that the test is affected by mechanical forces, exerted by
inner -- thethering mesenterial threads -- and outer -- tubefeet
muscles and the mechanical properties of the collagen fibers that
connect the test plates. Under low mechanical activity the test tends
to be globular, while under strong adherence the test is flat.
 A chemically decalcified dead
sea-urchin retains its shape, proving that the overall shape of the
sea-urchin is supported by the pneumatic properties of the soft tissue. A chemically decalcified dead
sea-urchin retains its shape, proving that the overall shape of the
sea-urchin is supported by the pneumatic properties of the soft tissue.
A special emphasis in my studies were
observations and experiments dealing with the skeleton growth and
calcification of the test, trying to demonstrate the influence of
mechanical pressure and forces applied by the contractile and --
tissues on the final shape. I showed that even without the support of
the hard plates, the sea urchin form retains it typical shape, due to
the soft tissue envelope, which acts as a matrix to the calcium
carbonate plates. An evidence to the pneumatic hypothesis is the
"soap-bubble" curvature pattern of the plates' edge, indicating that
inner pressure and outer surface tension of the plates' envelope are
primary to the calcification process. This and other evidence urged me
to propose a "bio- mechanical" model for the growth and morphogenesis
of sea urchins (ref. 10). The model was tested experimentally by
various scientists.
|
|
 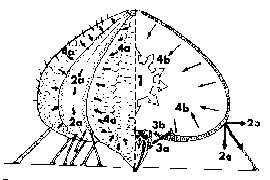 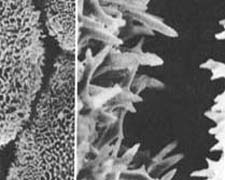
Left: the reversal curvature pattern of
echinoid skeletal plates, showing in the plate edge and earlier
growth-lines. Right: a gap between two neighboring plates in a living
test, induces rapid growth of needle-like 'trabeculae', proving that
available space enhances rapid growth. Middle: graphic presentation of
the "mechanical model".
|

Two types of deformed
T. gratilla under pollution

|
Deformities of
sea-urchin under pollution conditions.
Mass-deformities
(up to 70% urchins were affected) of two types were shown in Tripneustes
gratilla under pollution conditions, in the Gulf of Eilat. The
apparent cause seems to be chemicals aiming to prevent calcium
carbonate clogging of pipe systems in a local power-plant (ref. 2) or
hotel laundry (6). The deformities are believed to result from less
calcification and softening of the mechanical tissues - inter-plate
collagen fibers, inner muscles etc. These observations seem to support
the proposed model.
|
|

|
The biology of marine
mollusca
The Gulf of
Eilat (Aqaba) has a typical Indo-Pacific fauna, with large amount of
endemism. Pollution in the northern part of the Gulf limits the number
of living species. I have followed the Gulf mollusc fauna for over
thirty years, and published semi-popular reports and lists. I have also made a webguide to the mollusca of the region. .
|
 |
The effect of pollution on the
species diversity
I studied the
species diversity of invertebrate community on dead stony corals,
aiming to demonstrate the influence of pollution on the community (ref.
11).
|
|

 n n

|
Guiding and teaching nature
I have served many
years as warden and guide in the Nature Conservation organization, the
Society for the Protection of Nature, I dedicated much effort to the
develope a didactic approach to field teaching and study. I wrote many
articles -- in Hebrew -- on this topic.
Invertebrate web guides
I wrote several web
guides to the invertebrates of the Gulf of Eilat (Aqaba) all included in Dafni-sites:
Corals -
https://www.dafni.com/corals/index.htm
non-coral coelenterates - https://www.dafni.com/non-corals/index.htm
Echinodermata - https://www.dafni.com/echinodermata/index.htm
mollusca -
https://www.dafni.com/mollusca/index.htm
Crustacea - https://www.dafni.com/crustacea/index.htm
Tunicates - https://www.dafni.com/tunicata/index.htm
Worms - https://www.dafni.com/vermes/index.htm
Sponges - https://www.dafni.com/spongia/index.htm
Sea plants - https://www.dafni.com/plants/index.htm
Fishes - https://www.dafni.com/fish/index.html
|
|
SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS
1979-2010  = PDF העתקי
= PDF העתקי
 Ben-Eliahu,
N. & J. Dafni (1979) A new reef building serpulid genus and
species from Elat and the Red Sea, with notes on other gregarious tube
worms from Israeli waters.Isr. J. Zool. 28:199-208. Ben-Eliahu,
N. & J. Dafni (1979) A new reef building serpulid genus and
species from Elat and the Red Sea, with notes on other gregarious tube
worms from Israeli waters.Isr. J. Zool. 28:199-208.  Dafni,
J.(1980) Abnormal growth patterns in the sea urchin Tripneustes
cf. gratilla (L.) under pollution (Echinodermata:
Echinoidea). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 47:259-279. Dafni,
J.(1980) Abnormal growth patterns in the sea urchin Tripneustes
cf. gratilla (L.) under pollution (Echinodermata:
Echinoidea). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 47:259-279.  Dafni,
J. (1982) Skeletal deformations in the sea urchin Tripneustes
gratilla (L.) under pollution conditions in the Gulf of
Eilat, Red Sea. in: Echinoderms - Proceeding of the
Fourth International Conference,Tampa Bay, September 1981 (Ed. J.M.
Lawrence), A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam. pp. 69. Dafni,
J. (1982) Skeletal deformations in the sea urchin Tripneustes
gratilla (L.) under pollution conditions in the Gulf of
Eilat, Red Sea. in: Echinoderms - Proceeding of the
Fourth International Conference,Tampa Bay, September 1981 (Ed. J.M.
Lawrence), A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam. pp. 69.  Dafni,
J.& J. Erez (1982) Differential growth in Tripneustes
gratilla (Echinoidea). in: Echinoderms: Proceeding
of the Fourth Intenational Conference, Tampa Bay, September
1981(Ed. J.M. Lawrence), A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam. pp . 71-75. Dafni,
J.& J. Erez (1982) Differential growth in Tripneustes
gratilla (Echinoidea). in: Echinoderms: Proceeding
of the Fourth Intenational Conference, Tampa Bay, September
1981(Ed. J.M. Lawrence), A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam. pp . 71-75.  Dafni,
J. (1983a) A new sub-species of Tripneustes gratilla (L.)
from the northern Red Sea (Echinodermata: Echinoidea: Toxopneustidae). Isr.
J. Zool., 32:1-12. Dafni,
J. (1983a) A new sub-species of Tripneustes gratilla (L.)
from the northern Red Sea (Echinodermata: Echinoidea: Toxopneustidae). Isr.
J. Zool., 32:1-12.  Dafni,
J.(1983b) Aboral depressions in the tests of the sea urchin Tripneustes
cf. gratilla (L.) in the
Gulf of Eilat, Red Sea. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol.,
67:1-15 Dafni,
J.(1983b) Aboral depressions in the tests of the sea urchin Tripneustes
cf. gratilla (L.) in the
Gulf of Eilat, Red Sea. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol.,
67:1-15 Dafni,
J.& A. Diamant (1984) School-oriented mimicry, a new type of
mimicry in fishes. Mar.Ecol. Prog. Ser., 20:45-50. Dafni,
J.& A. Diamant (1984) School-oriented mimicry, a new type of
mimicry in fishes. Mar.Ecol. Prog. Ser., 20:45-50.  Dafni,
J. (1985) Effect of mechanical stress on the calcification pattern in
regular echinoids. in: Echinodermata - Proceeding of the
Fifth International Echinoderm Conference, Galway, September
1984 (Eds. B.E. Keegan and B.D.S. O'Connor), A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam.
pp. 233-236. Dafni,
J. (1985) Effect of mechanical stress on the calcification pattern in
regular echinoids. in: Echinodermata - Proceeding of the
Fifth International Echinoderm Conference, Galway, September
1984 (Eds. B.E. Keegan and B.D.S. O'Connor), A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam.
pp. 233-236.  Dafni,
J. (1986a) A biomechanical model for the morphogenesis of echinoid
tests. Paleobiology, 12:143-160. Dafni,
J. (1986a) A biomechanical model for the morphogenesis of echinoid
tests. Paleobiology, 12:143-160. - Dafni, J.
(1986b) Echinoid Skeletons as Pneu Structures. Konzepte SFB 230,
Universitat Tubingen und Stuttgart. Stuttgart, 13:9-96.
 Dafni,
J.& L. Fishelson (1986) Effect of pollution on the community
structure of animals associated with dead corals in Eilat (Gulf of
Aqaba, Red Sea). In: Environmental Quality and Ecosystem
Stability, Proc. Third Intern. Conf. of the Israeli Ecological Society,
(Ed. Z. Dubinsky & Y. Steinberger). Bar Ilan University Press,
Ramat Gan, Israel. Vol III/B; pp. 849-858. Dafni,
J.& L. Fishelson (1986) Effect of pollution on the community
structure of animals associated with dead corals in Eilat (Gulf of
Aqaba, Red Sea). In: Environmental Quality and Ecosystem
Stability, Proc. Third Intern. Conf. of the Israeli Ecological Society,
(Ed. Z. Dubinsky & Y. Steinberger). Bar Ilan University Press,
Ramat Gan, Israel. Vol III/B; pp. 849-858.  Dafni,
J.& R. Tobol. (1986/87) Population structure patterns of a
common Red Sea echinoid (Tripneustes gratilla elatensis)/Isr.
J. Zool., 34:191-204. Dafni,
J.& R. Tobol. (1986/87) Population structure patterns of a
common Red Sea echinoid (Tripneustes gratilla elatensis)/Isr.
J. Zool., 34:191-204.  Dafni,
J.& J. Erez (1987a) Skeletal calcification patterns in the sea
urchin Tripneustes gratilla elatensis: I. Basic
patterns. Mar. Biol. 95:275-287. Dafni,
J.& J. Erez (1987a) Skeletal calcification patterns in the sea
urchin Tripneustes gratilla elatensis: I. Basic
patterns. Mar. Biol. 95:275-287.  Dafni,
J.& J. Erez (1987b) Skeletal calcification patterns in the sea
urchin Tripneustes gratilla elatensis: II. Effect
of various treatments. Mar. Biol. 95:289-297. Dafni,
J.& J. Erez (1987b) Skeletal calcification patterns in the sea
urchin Tripneustes gratilla elatensis: II. Effect
of various treatments. Mar. Biol. 95:289-297.  Dafni,
J. (1988) A biomechanical approach to the ontogeny and phylogeny of
echinoids. in: C.R.C. Paul & A.B. Smith (Eds.)Echinoderm
Phylogeny and Evolutionary Biology. Oxford University Press,
Oxford. pp. 175-188.
Dafni,
J. (1988) A biomechanical approach to the ontogeny and phylogeny of
echinoids. in: C.R.C. Paul & A.B. Smith (Eds.)Echinoderm
Phylogeny and Evolutionary Biology. Oxford University Press,
Oxford. pp. 175-188.  Dafni,
J. (1992) Growth rate of the sea urchin Tripneustes gratilla
elatensis. Isr. J. Zool., 38:25-33. Dafni,
J. (1992) Growth rate of the sea urchin Tripneustes gratilla
elatensis. Isr. J. Zool., 38:25-33. - Dafni, J.
(1995) The need for Damaged Reef Reclamation and Restoration. In: Proc.
International Conference: The Ecosystem of the Gulf of Aqaba
in Relation to the enhanced Economical Development and the Peace
Process II - Eilat, Jan 30th - Feb 2nd, 1995, 84-86
- Dafni, J.
(2001) Reduced biodiversity in the northern Gulf of Eilat. Paper
prepared for the evaluation committee and presented at the IUI seminars
on May 2, 2001. 7 pp.
 Dafni,
J. (2008) Diversity and Recent Changes in the Echinoderm Fauna of the
Gulf of Aqaba with emphasis on the Regular Echinoids. in: F. D. Por
(Ed.) Aqaba-Eilat, the Improbable Gulf : Environment,
Biodiversity and Preservation. Magnes Press Jerusalem 2008
pp. 226-234.
Dafni,
J. (2008) Diversity and Recent Changes in the Echinoderm Fauna of the
Gulf of Aqaba with emphasis on the Regular Echinoids. in: F. D. Por
(Ed.) Aqaba-Eilat, the Improbable Gulf : Environment,
Biodiversity and Preservation. Magnes Press Jerusalem 2008
pp. 226-234.  Dafni,
J. (2010) Pollution induced mass-deformities in Tripneustes:
Biomechanical aspects. in: Echinoderms: Durham
Proceedings of the 12th International Echinoderm Conference, Durham,
New Hampshire, USA, 7-11 August 2006 (Eds L.G. Harris, S.A. Bottger,
C.W. Walker and M.P. Lesser), CRC Press, A Balkema Book,ISBN
978-0-415-40819-6, pp.601-607. Dafni,
J. (2010) Pollution induced mass-deformities in Tripneustes:
Biomechanical aspects. in: Echinoderms: Durham
Proceedings of the 12th International Echinoderm Conference, Durham,
New Hampshire, USA, 7-11 August 2006 (Eds L.G. Harris, S.A. Bottger,
C.W. Walker and M.P. Lesser), CRC Press, A Balkema Book,ISBN
978-0-415-40819-6, pp.601-607.
|
|
Popular publications
|
. |
"
Routes and Trails in the Eilat Region"
Gefen
Publications, Jerusalem (1995).
A guide book describing 30 foot
and car trails in the mountains of Eilat
Region:
|
. |
"Strange is their middle name - Echinodermata
inernet
book (PDF) describing the Echinoderms, and the story of a study made by
the author in the years 1979-1988"
|
 |
"Gulf of Eilat from the Red Sea to the Red Line..."
Cherikover, Tel
Aviv (2000).
A
comprehensive description of the Gulf of Aqaba-Eilat Gulf including
Geology, Biology, history and environmental aspects, (in Hebrew
only)
|
. |
"
Eilat's Coral Reefs"
Yeela Books,
Eilat (2008).
A guide and description of the coral reefs of Eilat, showing > 500 species of corals, invertebrates and fishes
|
|







